All Departments
- Adenoidectomy
- Ear Infection
- Eardrum Surgery
- FESS ( Functional-Endoscopic-Sinus-Surgery)
- Mastoidectomy Surgery
- Myringotomy
- Nasal Polyps Surgery
- Septoplasty
- Sinus Surgery
- Stapedectomy
- Throat Surgery
- Thyroidectomy
- Tonsillectomy
- Tonsillectomy
- Turbinate Reduction
- Tympanoplasty
- Vocal Cord Surgery
Emergency Cases
917838450942
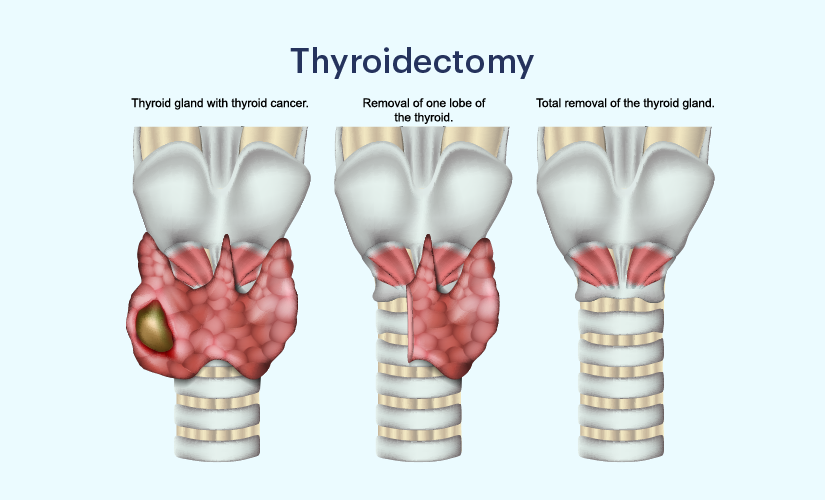
Thyroidectomy
Best ENT clinics for thyroidectomy surgery near you
One of India’s biggest and best surgical service providers is Doxtreat Healthcare. We offer cutting-edge care for a range of disorders, including thyroid disease and other ENT issues, because of our extensive surgical network.
A team of knowledgeable ENT doctors with more than 10 years of expertise in diagnosing, treating, and managing head and neck issues can be found at Doxtreat Healthcare. We provide advanced thyroidectomy surgery that is less invasive and allows for a complete recovery with few postoperative problems.
You can schedule a free consultation with one of our ENT doctors in a clinic close to you if you have thyroid problems and would like treatment. If you choose Doxtreat Healthcare for your care, you can also take advantage of other perks like complimentary cab rides, a no-cost EMI payment option, insurance support, etc.

What happens during a Thyroidectomy?
To ensure a successful surgery and a speedy recovery, the thyroidectomy surgery procedure starts with a thorough diagnosis. Before a thyroidectomy, the following diagnostic tests are carried out:
Physical exam: Your ENT expert will examine you physically, take a complete medical and family history, and evaluate the severity of your thyroid issues. Also, they will check your thyroid gland for any anomalies. They will recommend the appropriate imaging and diagnostic tests for you if there are any abnormalities.
Blood tests: Blood tests are used to measure the levels of the thyroid-stimulating hormones and the thyroxine (T4 hormone) in the blood, which can be used to identify the presence of thyroid problems.
Thyroid activity testing: A number of imaging procedures, including thyroid scans, radioiodine uptake tests, thyroid ultrasounds, etc., can be used to assess the thyroid’s degree of activity as well as the presence of cysts, nodules, or tumors.
Thyroid biopsy: Thyroid tissue may be removed during a biopsy to check for the presence of metastatic thyroid cancer if there is a suspicious development on the thyroid gland.
How to prepare for the surgery?
Major surgery like thyroidectomy is typically done under general anesthesia. The surgeon will conduct a number of imaging and diagnostic procedures prior to the procedure to ascertain how much thyroid tissue will be removed.
If you take blood thinners or other similar medications, you should cease using them at least a few days before to the procedure since this might raise the chance of problems.
You are not allowed to eat after midnight on the day of operation since it is done under general anesthesia. Moreover, make arrangements for someone to drive you home following the procedure.

When is a Thyroidectomy required?
If the patient is pregnant or unable to take anti-thyroid medications, thyroidectomy may be advised. The nature and severity of the thyroid problem determine how much of the thyroid gland needs to be removed. The following are the most typical causes of thyroidectomy:
Thyrotoxic cancer
thyroid gland enlargement that is not cancerous (goiter)
excessive thyroid activity (hyperthyroidism)
suspicious nodules developing on the thyroid gland

What are the complications associated with a Thyroidectomy?
- Infections: Postoperative infections are uncommon after thyroidectomy, but they can slow healing if they do occur. Following surgery, if there is an increase in pain, swelling, warmth, redness, pus drainage, or fever, this could be an indication of a surgical infection.
- Seroma: Seromas develop as a result of fluid buildup at the surgical site. When they are small, they go away in a few weeks, but if they are large, they must be surgically removed to avoid obstructing the airway.
- HypocalcemiaLow blood calcium levels, or hypocalcemia (hypoparathyroidism), are a frequent adverse effect after thyroid/parathyroid gland removal.
Patients must take calcium supplements for at least a week following surgery to manage this. Blood calcium levels are assessed at the first postoperative visit, and if they are normal, the patient may cease taking supplements.
- Persistent hoarseness/Voice change: The thyroid gland is placed near to the recurrent laryngeal nerve. A temporary hoarse voice, voice fatigue, and weakness may result from the surgery irritating the nerves. The resolution process might take a few weeks to six months. But, if the nerve is damaged, it will result in a voice that is permanently hoarse.
- Airway obstruction: Because the trachea was compressed during surgery, the patient can experience breathing difficulties. Usually, it goes away within the first 12 to 24 hours following surgery, but if it continues, it might cause hematoma development and other health issues.
How can I improve recovery after a Thyroidectomy?
The following advice can help you recover more quickly after your procedure:
Take good care of your wound. Each infection has the potential to impede recovery and cause new problems.
After surgery, take calcium supplements for at least a few weeks.
Before swimming or having a shower, check with your doctor.
To stop the scar from drying out and scabbing, apply creams to it.
During a few weeks, refrain from performing any vigorous activities or lifting anything heavy.
You should eat soft, simple-to-swallow meals while your surgery site is still stiff.
Water helps to soften food and avoid blockages, so drink enough of it before, during, and after meals.
You might require thyroid hormone replacements if you’re having a total thyroidectomy

